The Enigma of Pareidolia: The Mind’s Quest for Meaningful Patterns
In the mesmerizing interplay of light and shadow, our minds embark on a journey beyond the ordinary, seeking hidden treasures within random chaos. Enter the world of pareidolia, a captivating psychological phenomenon that unveils the human brain’s propensity to find familiar shapes and faces amid the seemingly indistinct and obscure. From the playful shapes of clouds to the curious marks on rocks, pareidolia leads us on a fascinating quest to discern the familiar in the enigmatic, pushing the boundaries of perception and imagination.
Beyond a mere trick of the mind, pareidolia is an enduring testament to the intricacies of human cognition and how we interpret the world around us. Drawing on the inherent human desire to recognize patterns and establish connections, this intriguing phenomenon transcends cultural boundaries, captivating minds across generations.
In this article, we embark on an enlightening journey into the depths of pareidolia, exploring the neurological underpinnings that drive our perceptions, and how this wondrous ability has both mystified and inspired humanity throughout history. From the ancient myths and tales born of celestial patterns to modern encounters with divine figures in the most mundane objects, pareidolia has left an indelible mark on our artistic expressions, spiritual beliefs, and even scientific pursuits.
Delving into the research and psychological theories behind this captivating phenomenon, we seek to shed light on why our minds yearn to find meaning in the random, and how these patterns illuminate the innate complexities of our thought processes.
So, fasten your seatbelts and prepare to embark on an intellectual adventure like no other as we unlock the secrets of pareidolia – an enchanting dance between the mundane and the mysterious, where the ordinary transforms into the extraordinary with a simple shift in perspective.
What is Pareidolia?
Pareidolia is a psychological phenomenon in which the human mind perceives familiar patterns or meaningful images in random or ambiguous stimuli, such as clouds, rocks, stains, or other visual textures. These perceived patterns are often recognizable as faces, animals, objects, or even religious or supernatural symbols.
The term “pareidolia” comes from the Greek words “para” (meaning “beside” or “alongside”) and “eidolon” (meaning “image” or “form”). It’s a type of illusion where the brain tries to make sense of the world by filling in missing information and finding recognizable shapes in the environment.
Pareidolia is not a form of mental illness; rather, it’s a natural consequence of how the human brain processes visual information. The brain is hardwired to recognize patterns and faces as a survival mechanism since identifying familiar objects or people quickly is crucial for social interaction and threat detection.
This phenomenon is not limited to visual stimuli alone; it can occur in other sensory modalities as well. For instance, people may perceive familiar sounds or voices in random noise or interpret ambiguous messages in a way that confirms their existing beliefs or expectations.
Pareidolia has been a subject of interest in various fields, including psychology, neuroscience, and even in discussions about extraterrestrial life. Some famous examples of pareidolia include seeing the “Man in the Moon,” perceiving animals or objects in cloud formations, and encountering religious figures on food items or natural formations.
Pareidolia is a fascinating aspect of human perception, and it reminds us of the complexity and adaptability of the human brain. However, it’s essential to recognize that these perceived patterns are products of our minds and not necessarily indicative of any actual underlying reality.
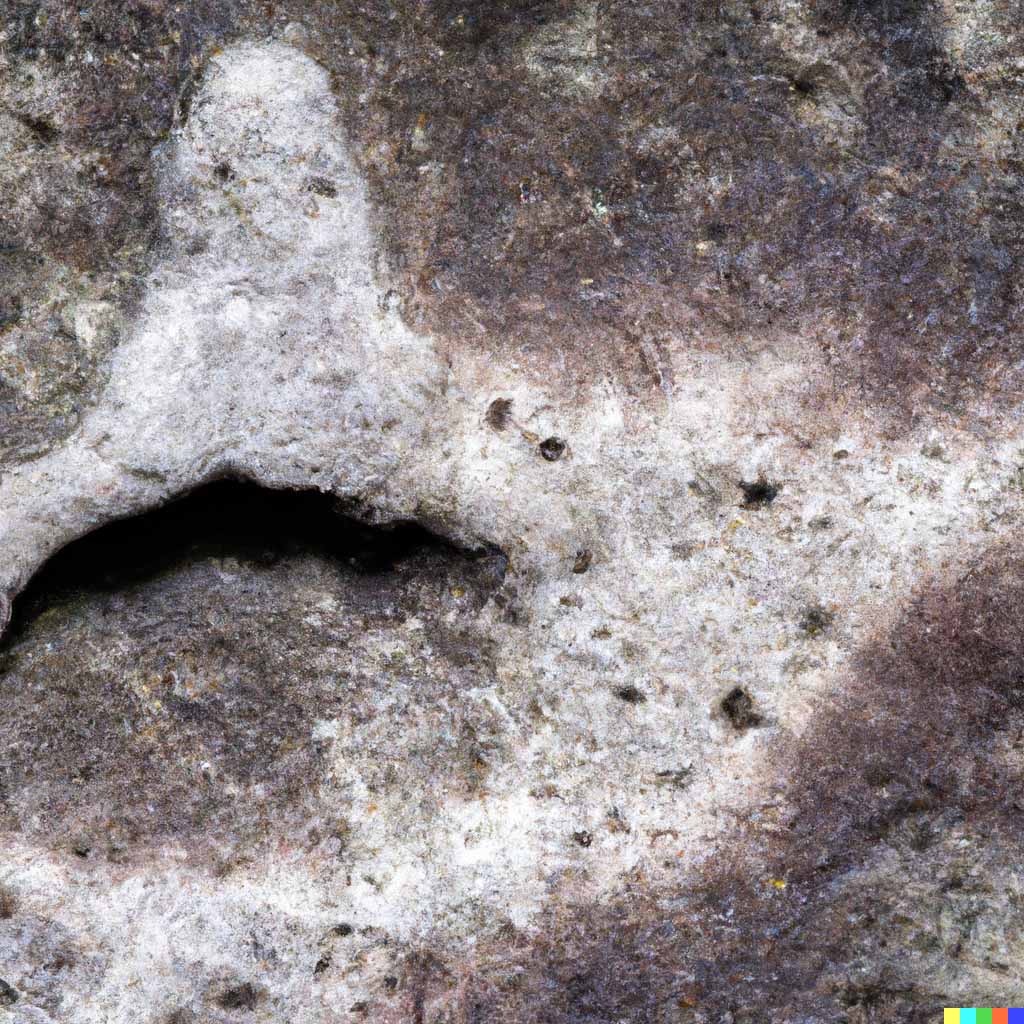

Is it rare to have Pareidolia?
No, pareidolia is not rare at all. In fact, it is a common and widespread phenomenon experienced by a significant portion of the population. As mentioned earlier, pareidolia is a natural consequence of how the human brain processes visual information and recognizes patterns. Our brains are hardwired to seek out familiar shapes and faces, which allows us to quickly identify objects and people in our surroundings.
Pareidolia occurs in people of all ages and cultural backgrounds. It can manifest in various ways, from seeing faces in clouds, animals in rock formations, or familiar shapes in random textures. You might have experienced it yourself without even realizing it.
Moreover, pareidolia is not limited to visual stimuli alone. It can occur in other sensory modalities, such as hearing familiar sounds or voices in random noise.
While pareidolia is a common phenomenon, the intensity and frequency of experiencing it may vary from person to person. Some individuals might be more prone to noticing meaningful patterns in ambiguous stimuli due to individual differences in brain processing and cognitive factors.
Overall, pareidolia is a fascinating aspect of human perception and a reminder of the complexity and adaptability of our minds. It’s a universal and intriguing phenomenon that has captured the curiosity of scientists, artists, and individuals alike throughout history.
Is pareidolia a Mental Disorder?
No, pareidolia is not a mental disorder. It is a normal and common psychological phenomenon that occurs in the human brain as a result of how we process visual information and recognize patterns.
As mentioned earlier, pareidolia is the tendency to perceive familiar shapes, faces, or meaningful patterns in random or ambiguous stimuli. This occurs because our brains are naturally wired to seek out and recognize patterns, including faces, as a way of efficiently processing and understanding the world around us.
Pareidolia is experienced by a large portion of the population and is not considered abnormal or pathological. It is a natural aspect of human perception and is not linked to any mental health condition or cognitive impairment.
It’s important to distinguish between normal psychological phenomena like pareidolia and actual mental disorders. Mental disorders are clinical conditions that significantly disrupt a person’s thoughts, emotions, behavior, or overall functioning, leading to distress or impairment in daily life. Examples of mental disorders include depression, anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, and others.
Pareidolia, on the other hand, is simply a quirk of how our brains work, and it doesn’t cause any harm or distress. In fact, it can be a fascinating and enjoyable experience for many people, sparking creativity and imagination.
In summary, pareidolia is a normal and intriguing aspect of human perception, not a mental disorder. It’s a reminder of the complexity and adaptability of our minds and is widely experienced by individuals without any clinical implications.
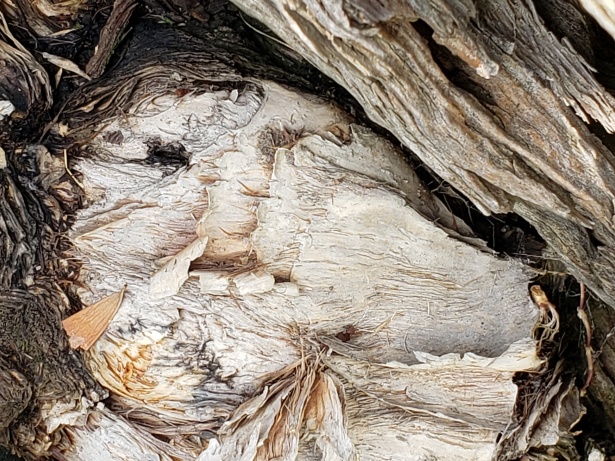

The Connection of Pareidolia and Paranormal
Pareidolia and the paranormal are intriguing topics that often intersect in the realm of human perception and belief systems. The human tendency to perceive meaningful patterns in random or ambiguous stimuli, known as pareidolia, has been a subject of fascination and curiosity throughout history. When it comes to the paranormal, this psychological phenomenon plays a role in how people interpret and experience what they perceive as supernatural or otherworldly occurrences.
In the context of the paranormal, pareidolia often manifests in reports of seeing apparitions, ghosts, or religious figures in various settings. For example, people may claim to have seen the image of the Virgin Mary on a piece of toast or the face of a deceased loved one in a photograph. These experiences are attributed to pareidolia, as the brain tries to find familiar patterns or faces even in seemingly random or vague visual stimuli.
Pareidolia has also been linked to reports of encountering unidentified flying objects (UFOs) or extraterrestrial beings. In some UFO sightings, witnesses describe seeing craft or creatures in the sky that resemble conventional flying objects or aliens from popular culture. However, skeptics often attribute these sightings to the misinterpretation of natural phenomena, such as clouds, weather balloons, or airplanes, due to the brain’s inclination to perceive familiar shapes and objects.
It is essential to acknowledge that while pareidolia may play a role in some paranormal experiences, it does not negate the possibility of genuine supernatural occurrences or phenomena that have not yet been fully understood or explained by science. Human perception is complex, and our brains sometimes attempt to make sense of the unknown by fitting it into recognizable patterns or concepts.
The interplay between pareidolia and the paranormal is a subject of ongoing research and debate in fields such as psychology, cognitive science, and parapsychology. Understanding the mechanisms behind pareidolia can help us recognize when our perceptions might be influenced by this phenomenon, leading to more critical evaluations of purported paranormal experiences.
Paranormal Examples of Pareidolia
Paranormal examples of pareidolia often involve people perceiving supernatural or otherworldly entities in everyday objects or natural phenomena. These instances can evoke feelings of mystery, awe, and fear, leading to various interpretations and beliefs. While skeptics attribute such occurrences to pareidolia and the brain’s tendency to find familiar shapes in random stimuli, those who believe in the paranormal may see these events as evidence of ghostly or spiritual presence. Here are a few paranormal examples of pareidolia:
- Ghostly Apparitions: People often claim to see ghostly figures or apparitions in photographs or videos, especially in places with a reputation for being haunted. These perceived entities might appear as translucent figures, shadows, or mist-like forms. However, many of these images can be attributed to pareidolia, where the brain interprets patterns of light and shadows as human-like shapes.
- Faces in Haunted Locations: Visitors to reputedly haunted locations sometimes report seeing faces or figures in walls, mirrors, or windows that they believe are connected to spirits or supernatural entities. These sightings are often associated with strong emotions and a belief in the paranormal.
- EVP (Electronic Voice Phenomenon): EVP is a paranormal phenomenon where people claim to capture ghostly voices or messages on audio recordings, often using devices such as digital voice recorders. Skeptics argue that these mysterious sounds are merely random noise or electronic artifacts that the brain interprets as meaningful speech.
- Spirit Photography: In the past, during the spiritualism movement, people claimed to capture images of deceased loved ones or spirits in photographs, known as spirit photography. These photographs often featured vague, misty forms or faces, which some attributed to the presence of spirits. However, investigations have revealed that these effects could be achieved through double exposure or other photographic techniques.
- Orbs in Photographs: Orbs are circular, glowing anomalies that appear in flash photography. Some people believe these orbs represent spirits or energy entities. However, orbs are commonly caused by dust, water droplets, insects, or other particles reflecting light from the camera flash.
- Shadow People: Some individuals claim to see dark, humanoid silhouettes moving around their peripheral vision or within dimly lit areas. These entities are often referred to as “shadow people.” While paranormal enthusiasts believe they are spirits or interdimensional beings, scientists and skeptics attribute these sightings to pareidolia and the brain interpreting shadows as recognizable shapes.
It’s important to emphasize that while these paranormal examples of pareidolia have captured the attention of believers and enthusiasts, scientific evidence supporting the existence of ghosts, spirits, or other supernatural entities remains inconclusive. Investigations into these phenomena typically reveal natural explanations or illusions that result from the way our brains process sensory information.

Famous Examples of Pareidolia
There are several famous and well-known examples of pareidolia that have captured the public’s imagination over the years. Some of these examples have become iconic and even sparked cultural or religious significance. Here are a few notable ones:
- “Man in the Moon“: One of the most recognized examples of pareidolia is the perception of a face on the surface of the Moon. When looking at the full moon, many people see what appears to be a human face gazing back at them. This phenomenon has been observed across different cultures and is an enduring image in folklore and storytelling.
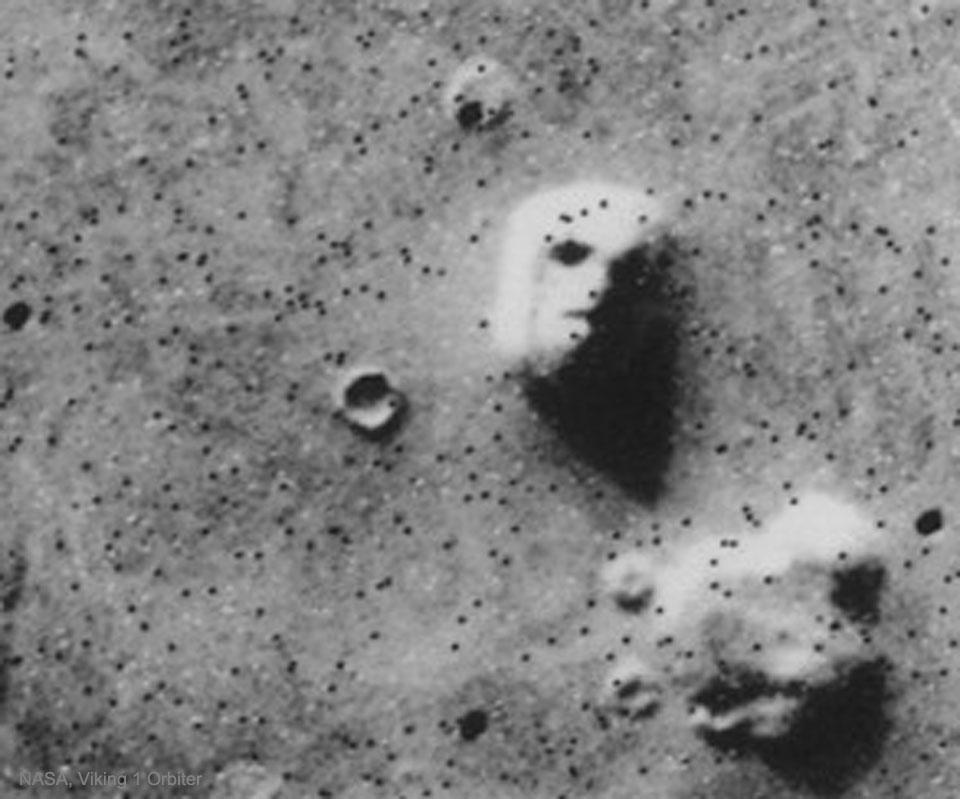
- Face on Mars: In 1976, NASA’s Viking 1 spacecraft captured an image of the Martian surface that seemed to show a formation resembling a human face. The “Face on Mars” image sparked widespread speculation about the possibility of an ancient alien civilization on the red planet. Subsequent high-resolution images from other Mars missions revealed that the face-like formation was just a natural rock formation with no significance.
- The Shroud of Turin: The Shroud of Turin is a piece of cloth that bears the faint image of a man with wounds similar to those described in Christian tradition as those of Jesus Christ. Believers consider it to be the burial shroud of Jesus. Skeptics, on the other hand, attribute the image to a form of pareidolia, possibly created through a combination of factors, including the way the cloth was woven and the natural aging processes of the linen.
- “Mars Rat“: In 2012, during NASA’s Mars Curiosity mission, a photo taken by the rover showed a rock formation that some enthusiasts believed resembled a small rodent or “Mars rat.” The image quickly gained attention on social media, with some suggesting it was evidence of life on Mars. However, the “rat” was later identified as just a rock with coincidental shadows and angles.
- “Virgin Mary Grilled Cheese Sandwich“: In 2004, a woman in the United States claimed that she saw the image of the Virgin Mary on a grilled cheese sandwich she had made ten years earlier. The sandwich subsequently became a famous item on online auction sites, with bidding reaching thousands of dollars before it was finally sold.
These examples illustrate how pareidolia can occur in various contexts, from celestial bodies to religious artifacts and even in extraterrestrial exploration. They also highlight the cultural and emotional significance that can be attached to such perceived patterns, shaping beliefs and inspiring creative interpretations.

















































Leave a Reply